Dedicated 3D printing hub answers the call.
The immediacy and importance of Sétif’s need caused Alstom to engage its own dedicated 3D printing hub for a solution. Part of the company’s “Industry of the Future” program, the operation designs and produces 3D printed parts for its customers quickly and cost-effectively – for new trains or maintenance requirements on existing rolling stock. Having this in-house production capability on-demand has significantly increased Alstom’s digital supply chain efficiency, minimizing its dependency on external suppliers – with over 32,000 parts 3D printed since its creation in 2016.
To address the issue, Alstom turned to the facility’s Stratasys F370™ 3D Printer. The additive manufacturing team developed a design for a rubber-like plug to seal the holes in the trams’ headlights and provide a rapid and effective means of preventing further foreign object damage.
In order to functionally test the plugs in a reallife environment, the team 3D printed the parts using Stratasys’ durable elastomer material, FDM® TPU 92A thermoplastic polyurethane. Combining flexibility and stretch with abrasion and tear resistance, FDM TPU 92A proved the ideal elastomeric material to withstand the rigors of sustained exterior use.

Deploying Stratasys FDM technology, Alstom saved Sétif Tramways around 6,000 euros by 3D printing spare parts on-demand.
Looking ahead.
Advancements in additive manufacturing are growing constantly, allowing companies like Alstom to take control of their production and supply chain, to ensure customer service and satisfaction.
“The agility that additive manufacturing gives us is critical for Alstom strategically as a business,” continues Fussel. “Where customers such as Sétif Tramways depend on these parts to maintain operations, having this in-house production capability means we’re supply-chain independent. This makes it a game changer, as it ensures we can respond quickly and effectively with a solution to customers’ application requirements,” he concludes.
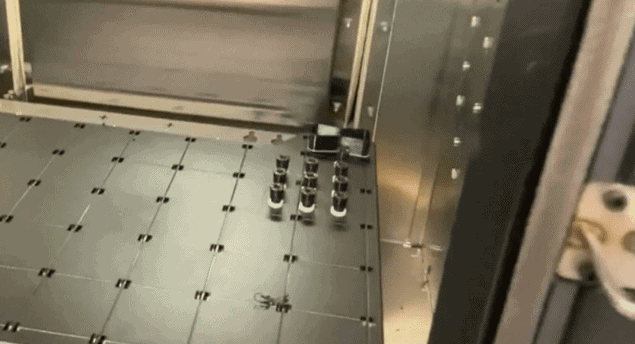
Using Stratasys FDM 3D printing, Alstom was able to design, produce and deliver a dozen highly durable stoppers within just 48 hours of receiving the request from Sétif.
Time-saving efficiencies
of 95%.
By 3D printing with FDM TPU 92A material, Alstom avoided expensive and time-consuming molding or casting methods to produce the parts. This would typically amount to several weeks in lead time for Sétif and several thousand euros fixed costs.
“To just create a rubber plug for trams, traditional manufacturing methods can take up to a minimum of three weeks alone,” explains Jaume Altesa, Barcelona 3D Printing Hub Manager at Alstom. “Leveraging our Stratasys FDM 3D printer, we were able to design, manufacture and deliver a dozen TPU rubber plugs to Sétif’s site within just 48 hours of the customer’s request – that’s an incredible time-saving of 95%.”
The speed at which Alstom was able to resolve its customer’s issue with an appropriate and functional solution is underscored by the fact that one part took less than 30 minutes to print, compared to the typical 3-week lead time via a traditional manufacturing process, collectively saving Sétif around 45 days of lead time.
The efficiency benefits not only relate to time but cost too. With traditional subtractive production methods, around 80% of materials goes to waste, but this is not the case with additive manufacturing. Using the F370s, Alstom saved around 6,000 euros fixed costs on the job for Sétif alone.
