Composite Analysis in SOLIDWORKS Simulation
SOLIDWORKS Simulation helps analyze symmetrical and unsymmetrical composite layups, as well as composite sandwiches. Each layer can be defined by a unique set of material properties and orientation, giving the designer maximum control to find the optimum layup and material for maximum product performance.
The failure criterion for composite materials is very different than for metals. Composite materials do not yield; rather, the fibers delaminate and fracture. SOLIDWORKS Simulation reports the FoS against failure according to the Tsai-Wu and Tsai-Hill failure indexes.
SOLIDWORKS Simulation uses FEA methods to discretize composite components into shell elements and uses stress analysis to determine the response of parts and assemblies due to the effect of forces, pressures, contact between components etc.
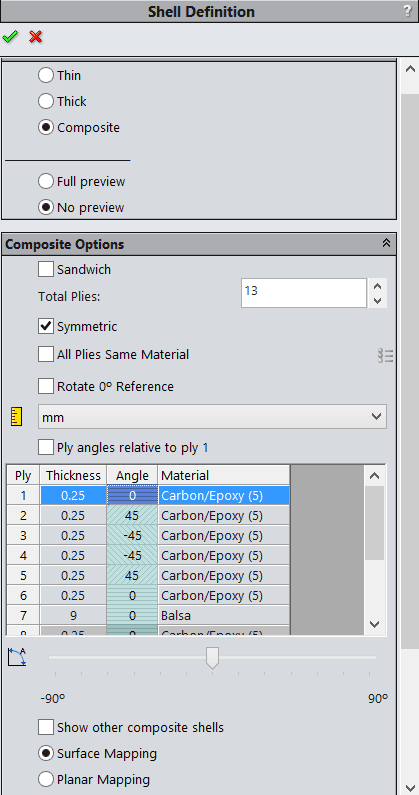
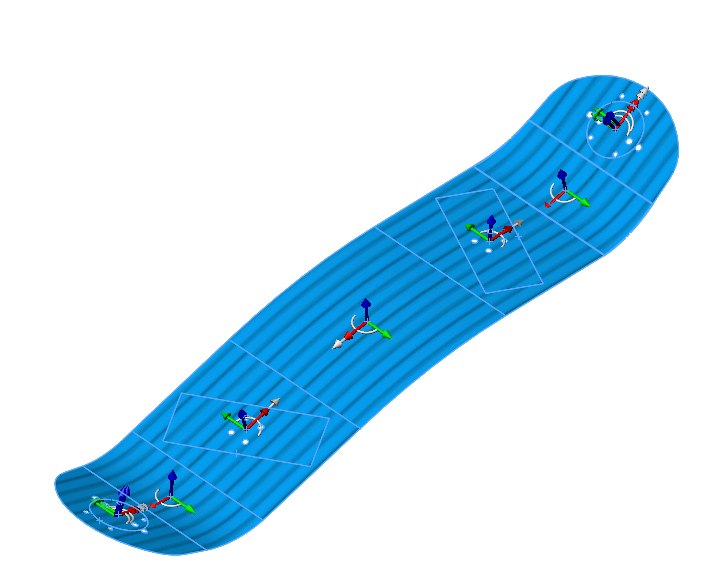
Stress plot displays the maximum stress values of the specified component (envelope plot) across all plies. The program includes the Top and Bottom faces while searching for the extreme value across all plies.
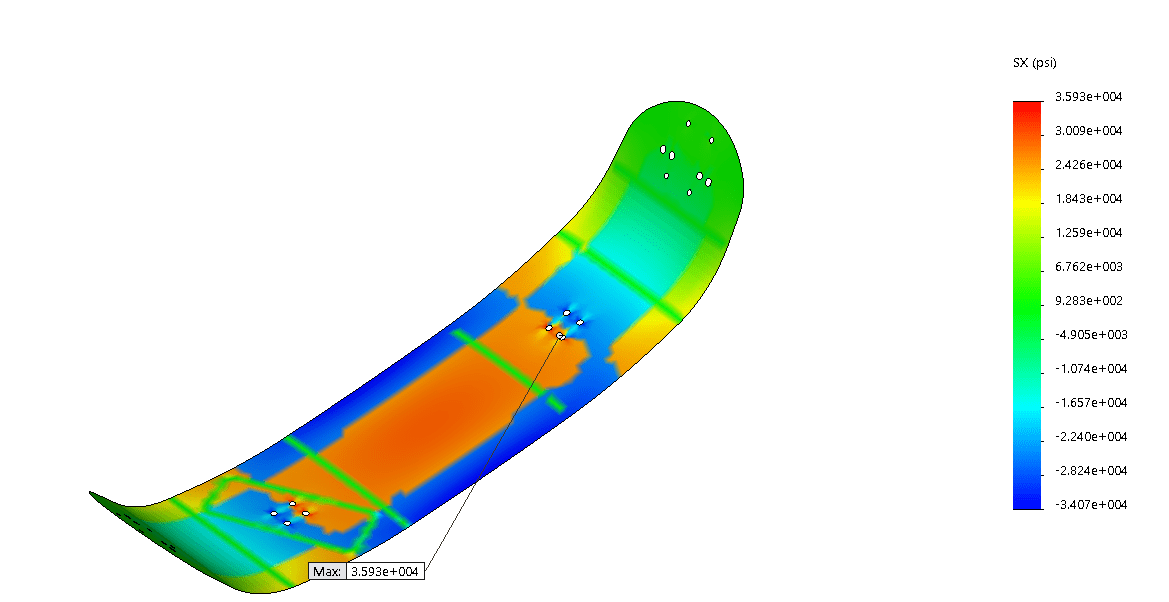
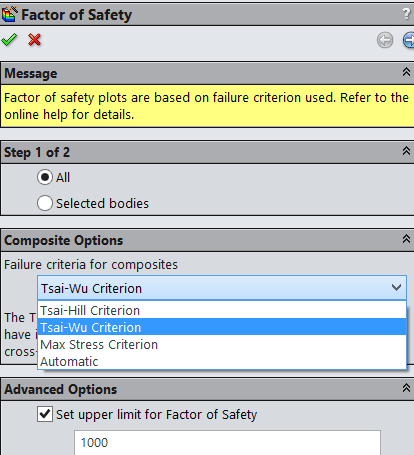
Tsai-Hill criteria is best applied to composite materials that have equal strengths in tension and compression and cross-fiber stress is primarily in tension.
The Tsai-Wu criteria is best applied to composite materials that have inequal strengths in tension and compression and the cross fiber stress is primarily in tension.
Max stress criteria is best applied to composite where the cross-fiber stress is primarily in compression.
To understand complex component responses with analysis of composite parts use SOLIDWORKS Simulation. You can then optimize material selection and the number and orientation of the composite ply layup to ensure quality, performance, and factor of safety (FoS).
Rajat Trehan
Product Manager
Computer Aided Technology Inc.

 Blog
Blog